Quick Summary: BIM software is becoming the standard for all public and private investment projects. Read this article to know why the current market is best to invest in BIM software. This blog is a comprehensive guide to BIM software including key elements, advantages, features, BIM working process, practical applications, stages, challenges and how we as a leading software development company can help you build extensive custom Building Information Modeling (BIM) software.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is at the heart of the transformation of the construction industry in this revolutionary journey. No longer a futuristic concept or optional tool, but a core pillar of national infrastructure strategies around the globe.
With the global BIM in construction market projected to grow from $2.5 billion in 2019 to over $7.5 billion by 2027, with a CAGR of 15%, the momentum is undeniable.
But exactly BIM is more than just software or 3D models, it is a collaborative process, mainly a human driven activity that redefines how buildings are designed, approved, constructed and maintained.
Major countries are setting the pace with bold permit procedures like E-Construction Action Plan and Digital Twins. This approach aims to automate permit procedures, increase transparency and manage real-time building conditions through digital platforms.
According to the Construction Long-Term View 2035, Within the next few decades, BIM is on track to become the standard for all public investment projects. Meaning, for governments, contractors, software developers and architects alike, Building Information Modeling (BIM) software development is not just a software but a transformation to a better and rapid world!
BIM Software Development: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025
In this blog, we’ll explore the aspects of BIM including its evolution, opportunities and technical foundations of BIM software development, and why more is the time for stakeholders to invest in smarter and more integrated digital software solutions that will not define the future of construction but make it more easier and identify the potential issues before they become a costly problems.
What is Building Information Modeling (BIM) Software Development?
Building Information modeling (BIM) software development refers to the creation and evolution of digital tools and platforms that allow construction professionals to plan, design, manage and execute building projects more efficiently and collaboratively.
But Building Information Modeling (BIM) isn’t just about the software, it is about a smarter methodology that supports data-driven decision making throughout the lifecycle of a construction project.
At its core, BIM brings together multiple disciplines architecture, engineering, construction and facility management onto a shared, intelligent 3D model. BIM plays a crucial role as a game-changing solution, when even the most well-planned projects face unexpected setbacks like miscommunication, condition failures and a lack of standardization often lead to costly delays and errors.
According to the European Construction Industry Federation, the broader adoption of BIM might provide 15-25% savings in the global infrastructure market. Even a 10% efficiency gain could inject €130 billion into Europe’s €1.3 trillion construction industry. This is not just optimization but production and revolution in value.
Particularly for construction managers, BIM software enables them to:
-
Coordinate seamlessly across teams,
-
Gather and interpret critical data for better decision making,
-
Visualize project outcomes before a single brick is laid,
-
Reduce risks and rework through early detection of design clashes,
-
Streamline workflows from planning to permitting to execution.
In the following section, you’ll explore what elements BIM software has, the features that drive its effectiveness, how businesses can leverage this technology to deliver better, faster and more cost-effective projects.
Read: Construction Management Software Development
9 Key Aspects of Building Information Modeling (BIM) Software Development
Here are the key aspects every successful BIM solution should include:
-
3D Modeling
-
Robust Data Management
-
Seamless Collaboration
-
Smart Analysis & Decision Support
-
Integrated Project Management
-
Design Visualization
-
Simulation Tools
-
Data Interoperability
-
User Interface & User Experience
Developing effective BIM software involves combining advanced technology with construction expertise to build seamless projects.
.avif)
 (1).avif)
-
3D Modeling: Allows the creation of detailed, data-driven digital representation of buildings that serves as the central hub for project information across all phases.
-
Robust Data Management: For better and easy access and consistency, it organizes and stores critical project data such as material specs, timeframes and cost estimates.
-
Seamless Collaboration: Enables real-time coordination between stakeholders (architects, engineers, contractors) through model sharing, change tracking and conflict resolution tools.
-
Smart Analysis & Decision Support: Offers tools like clash detection, cost analysis and energy modeling to improve design accuracy and support informed decision-making.
-
Integrated Project Management: Allows to track schedules, assign tasks and manage resources directly within the BIM environment which improves control and accountability.
-
Design Visualization: Provides interactive 3D visualizations to communicate designs clearly to clients and stakeholders which enhances understanding and engagement.
-
Simulation Tools: Allows performance testing of lighting, energy use, acoustics and more to help teams optimize designs before construction begins.
-
Data Interoperability: To ensure the smooth data exchange and avoid duplication or errors by supporting integration with other platforms for example CAD, ERP systems.
-
User Interface & User Experience: Provides an intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface to ensure accessibility for all project users, from designers to site managers.
Benefits of Building Information Modeling (BIM) Software Development
Here are the most impactful benefits BIM brings to the table:
-
Improved Project Visualization
-
Enhanced Collaboration
-
Enhanced Efficiency
-
Cost Reduction
-
Better Project Management
-
Improved Sustainability
-
Improved Quality
-
Reduced Risk
-
Better Facility Management
Building Information Modeling (BIM) software is evolving the way construction projects are planned, executed and managed.
.avif)
 (1).avif)
-
Improved Project Visualization: Stakeholders can easily visualize the project’s design, structure and layout with detailed 3D models. This approach helps identify design flaws and challenges early in the planning phase, reducing costly surprises during construction.
-
Enhanced Collaboration: BIM allows all stakeholders including architects, engineers, contractors and clients to work on a shared centralized digital model. The real-time collaboration boosts clearer communication, fewer misunderstandings and smoother coordination across discipline.
-
Enhanced Efficiency: BIM reduces duplication, minimizes errors and shortens project timelines by streamlining workflows by automating routine tasks and connecting different phases of construction.
-
Cost Reduction: BIM can significantly reduce rework and material waste by detecting issues before construction starts and optimizing the planning process. This leads to better cost control and improved ROI.
-
Better Project Management: Building Information Modeling (BIM) software helps teams track progress, allocate resources and manage timelines and budgets with integrated tools. This ensures better oversight and more successful project delivery.
-
Improved Sustainability: Early in the design stage, BIM enables teams to simulate and analyze building performance like energy consumption and material usage. This supports the creation of greener and more sustainable buildings.
-
Improved Quality: BIM minimizes errors and inconsistencies with greater accuracy in planning and modeling leads to higher quality designs and builds. This results in more reliable outcomes.
-
Reduced Risk: The software helps identify and assess potential risks like structured issues, safety hazards, budget overruns before they escalate. This proactive approach reduces uncertainty during execution.
-
Better Facility Management: BIM models serve as a valuable asset for facility management once construction is complete. They provide detailed insights into building components, systems and maintenance needs. This improves long-term operational efficiency.
Read: Most Popular Types of Software Development
Core Features of Building Information Modeling (BIM) Software
Below are the core features to consider when developing or choosing BIM software:
-
Design Visualization & Simulation
-
Coordination and Collaboration
-
Project Management Integration
-
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
-
Facility Management Features
-
Interoperability & Open Standards
-
User Experience & Accessibility
Developing high-quality BIM software demands careful attention to the features that drive efficiency, collaboration and long run value. From the design phase to facility management, BIM tools serve as powerful enablers for architects, engineers, contractors and building operators.
1. Design Visualization & Simulation:
-
3D BIM Modeling: The foundation of any BIM solution is its ability to create rich, data-driven 3D models that represent the physical and functional aspects of a building. These models offer stakeholders a clear visual understanding of the design, fostering smarter decision making early in the project.
-
Design Simulations: Integrating simulations for key performance aspects such as lighting, airflow, energy usage, thermal performance and even acoustic modeling in advanced BIM software. These tools allow designers to test various scenarios and make adjustments before construction begins. This ensures optimal building efficiency and occupant comfort.
.avif)
2. Coordination and Collaboration:
-
Team Collaboration Tools: Features like version control, shared access and model markup capabilities help reduce communication gaps and improve workflow consistency. Effective BIM software supports real-time collaboration between multidisciplinary teams which ensures that architects, engineers and contractors are always working from the same data set.
-
Clash Detection: Clash detection automatically identifies design conflicts like overlapping HVAC systems and structural components before they turn into costly on site issues. Early conflict resolution results in fewer delays, lower costs and higher build quality.
 (1).avif)
3. Project Management Integration:
-
Cost & Scheduling Estimations: Built-in tools for estimating project costs and timelines allow stakeholders to better plan budgets, reduce overruns and monitor progress. These tools offer unmatched control over project scope and execution when paired with historical data and predictive analytics.
-
AI-Driven Resources Management: Modern BIM solutions leverage AI and machine learning to forecast labor, material requirements and equipment availability. This predictive capability enhances resource allocation, lower waste and ensures that project deadlines are met efficiently.
 (1).avif)
4. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability:
-
AI & IoT Integration for Green Building: BIM software can continuously monitor and optimize energy performance by integrating with IoT devices and AI algorithms. It can simulate material impacts, water usage and carbon emissions. This helps teams make environmentally responsible decisions aligned with LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and other sustainability standards.
-
Lifecycle Analysis: BIM extends beyond design and construction into long term lifecycle analysis. It collects data for future renovations, retrofitting and even decommissioning, supporting more sustainable and cost-effective building management over decades.
 (1).avif)
5. Facility Management Features:
-
Post-Construction Digital Twin & Database: BIM software can function as a digital twin, a living, evolving model that tracks the performance and maintenance of the building once the building is complete. Facility managers can use it to monitor HVAC systems, optimize space utilization and plan maintenance schedules efficiently.
-
Asset & Space Tracking: With comprehensive asset tracking such as lighting systems, plumbing and machinery and space management. This results in more efficient operations and reduced long-term costs.
 (1).avif)
6. Interoperability & Open Standards:
-
Integration With Other Systems: BIM software seamlessly integrates with tools like CAD, ERP, GIS and project management platforms. Support for open standards such as IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) ensures compatibility across different systems and stakeholders.
 (1).avif)
7. User Experience & Accessibility:
-
Intuitive UI/ UX Design: BIM software can provide a diverse range of users from design professionals to site supervisors. A user-friendly interface, customizable dashboards and responsive navigation are essential for encouraging widespread adoption.
-
Mobile Accessibility: On-site access to BIM data via mobile apps or tablets ensures that construction managers and technicians make real-time decisions, check specifications and report issues right from the field.
.avif)
Read: Key Features to Look for in a Software Development Company
Building Information Modeling (BIM) Software Process
BIM software is not just a 3D modeling tool but a robust process that spans the entire lifecycle of a building project. BIM allows collaboration, enhances efficiency and ensures informed decision making at every stage from initial planning to eventual demolition.
Phase 1: Planning Phase
In this planning stage, BIM utilizes reality capture technologies like 3D laser scanning and drone surveys to create accurate digital representations of existing conditions. This data aids in site analysis, feasibility studies and environmental impact assessments. By simulating various scenarios, stakeholders can make informed decisions early in the project process.
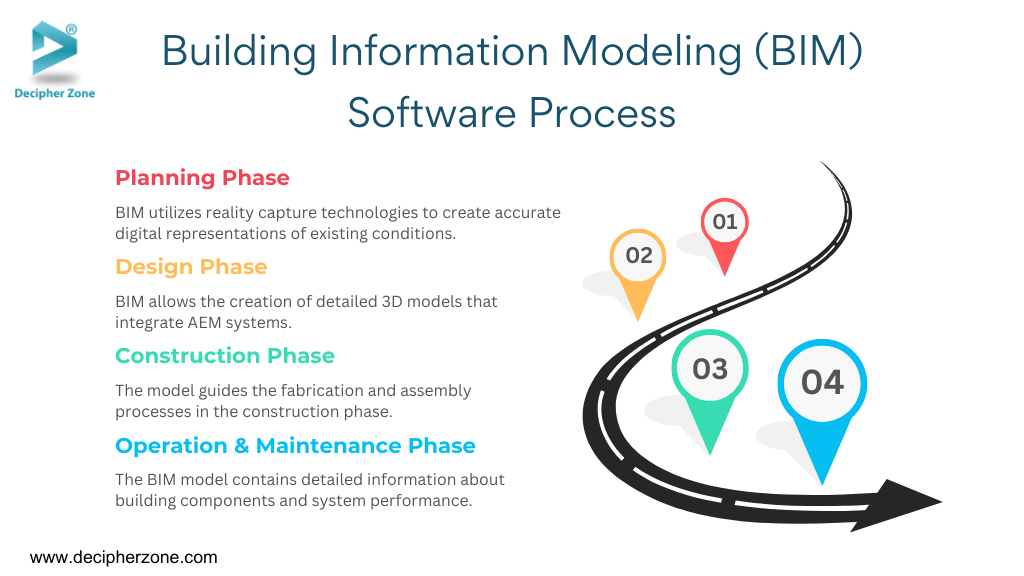
Phase 2: Design Phase
During design, BIM allows the creation of detailed 3D models that integrate architectural, structural and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing) systems. These models enable for clash detection which ensure different systems do not interfere with one another. BIM simplifies energy analysis, lighting simulations and cost estimates that leads to optimized designs.
Phase 3: Construction Phase
The model guides the fabrication and assembly processes in the construction phase. They provide precise information for prefabrication, scheduling and logistics which reduce waste and minimizes delay. Real-time updates help all the stakeholders to work with the most current information on the BIM model.
Transform your design process—build smarter with our cutting-edge BIM software. Start your free trial today!
Phase 4: Operation & Maintenance Phase
In the post-construction, BIM caters to a valuable tool for facility management. The BIM model contains detailed information about building components, maintenance schedules and system performance. Facility managers can use this data for preventive maintenance, further renovations and eventual deconstruction.
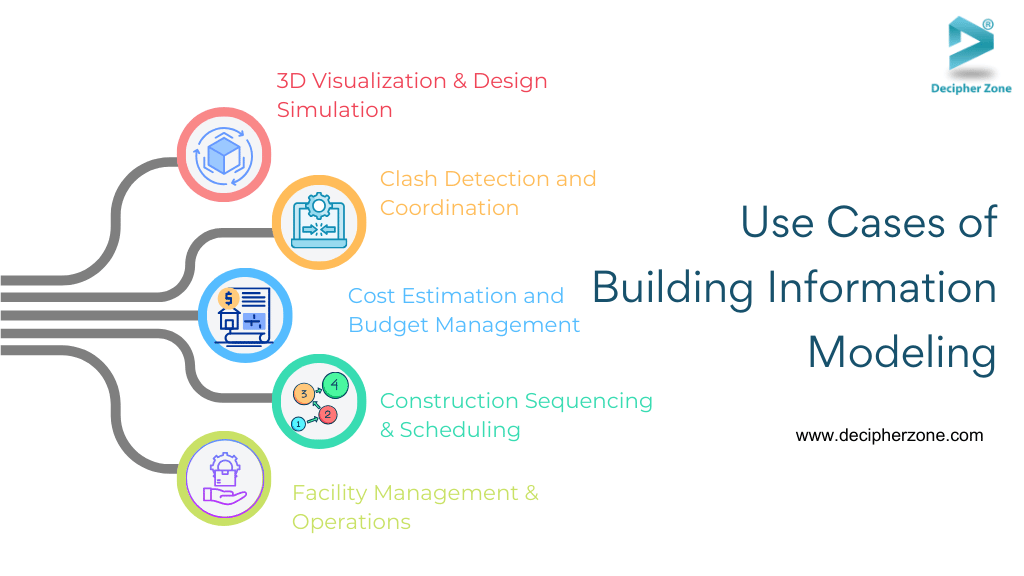
Use Cases of Building Information Modeling (BIM) Software
Here are the key use cases of Building Information Modeling (BIM):
-
3D Visualization & Design Simulation
-
Clash Detection and Coordination
-
Cost Estimation and Budget Management
-
Construction Sequencing & Scheduling
-
Facility Management & Operations
-
Streamlined Fabrication & Prefabrication Processes
-
Regulatory Compliance & Code Reviews
-
Sustainability & Energy Analysis
-
Disaster Planning and Emergency Management
This technology provides enhanced collaboration, efficiency and decision-making as we have seen in the earlier section throughout the building process.
1. 3D Visualization & Design Simulation
BIM allows developing detailed 3D models, allowing stakeholders to visualize the building before construction begins. This helps in identifying design flaws early and reduce costly charges during construction.
2. Clash Detection and Coordination
BIM aids in detecting clashes between different systems by integrating architectural, structural and MRP (Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing) designs. This proactive approach minimizes rework and delays.
3. Cost Estimation and Budget Management
BIM allows for accurate quantity take-offs and cost estimations that help to improve budget management and financial planning the entire project process.
4. Construction Sequencing & Scheduling
Project managers can link the 3D model with the construction schedule through 4D BIM. This allows for efficient planning and monitoring of construction activities.
5. Facility Management & Operations
BIM provides detailed information about building components, maintenance schedules and system performance post construction. This supports efficient operations and maintenance strategies.
6. Streamlined Fabrication & Prefabrication Processes
The detailed BIM models are used to generate shop drawings and guide the fabrication of building components which supports off-site prefabrication, reducing waste and improving construction efficiency.
.avif)
7. Regulatory Compliance & Code Reviews
BIM models are used to ensure compliance with building codes and regulations that enable smoother approval processes with regulatory authorities.
8. Sustainability & Energy Analysis
BIM helps energy modeling and sustainability analysis that aids in designing buildings that are energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
9. Disaster Planning and Emergency Management
Integrating in BIM software in emergency planning enables the simulation of evacuation scenarios and disaster response strategies that boosts building safety.
Stages and Levels of Development in Building Information Modelling (BIM) Software
Here is a breakdown of the core levels of BIM that are shaping modern construction and infrastructure management:
-
Level of Development (LOD)
-
4th Dimension- Time
-
5th Dimension- Cost
-
6th Dimension- Sustainability
-
7th Dimension- Facility Management
Each level introduces additional layers of data and capabilities that allows project stakeholders to better manage design, construction, operation and maintenance throughout a building’s lifecycle. Understanding the various stages of Building Information Modelling (BIM) is crucial for leveraging its full potential.
1. Level of Development (LOD):
LOD defines the degree of detail and reliability of information within the BIM model at different project stages from conceptual design to as-built conditions.
The level of Development ensures that stakeholders can trust the accuracy of data as it progresses through phases like design, construction, facilities management. Standard LOD classifications such as LOD 100 to LOD 500 helps in maintaining clarity and expectations across teams.
Streamline coordination, reduce rework, and deliver on time. See how our BIM tools can revolutionize your next project—schedule a demo now!"
2. 4th Dimension- Time
4D BIM Model allows teams to visualize the construction sequence over time as it integrates scheduling data with the 3D model. This temporal dimension provides insights into project timeframes which allows better planning, resource allocation and conflict resolution before work begins on-site. The outcomes can be improved coordination, lower delays and boosted project delivery.
.avif)
3. 5th Dimension- Cost
5D BIM estimating is the 4D model that links financial data to building components. This allows the owner to know the exact amount the contractor is billing at the given time which is the ability to analyze and track cost as the design evolves.
By this, stakeholders can analyze the financial impact of changes in real-time. It helps project owners and managers keep budgets under control and avoid unexpected cost overruns.
4. 6th Dimension- Sustainability
The 6D model introduces environmental and energy performance data into the model as sustainability becomes a core priority in the construction industry. It allows simulation of energy usage, carbon emissions and process impacts of materials which supports informed decisions that contribute to eco-friendly building designs and long-term operational efficiency.
5. 7th Dimension- Facility Management
7th Dimension is devoted to facilities management and focuses on extending its value into operations and facility management. Sometimes it may be referred to as Asset Information Models (AIM).
It serves as a digital twin of the built environment, containing asset data, maintenance schedules and warranties. This allows facilities teams to manage operations, lower downtime and extend asset life with accurate and accessible information.
The Role of Standards in BIM Implementation
Building Information Modeling (BIM) implementation is guided by international and national standards to ensure consistency and interoperability. Mostly, ISO 19650, which provides a framework for managing information over the whole lifecycle of a build asset using BIM. More to ISO, many countries have established national standards and mandates to streamline BIM adoption across public and private sectors.
Read: Ensure Quality Software Development
Why It Matters
As each level of BIM adds significant value to actionable insights by transforming data. Contractor planning timelines, architect refining design accuracy or a facility manager can optimize maintenance and understand these stages to maximize efficiency, reduce costs and future proof the assets.
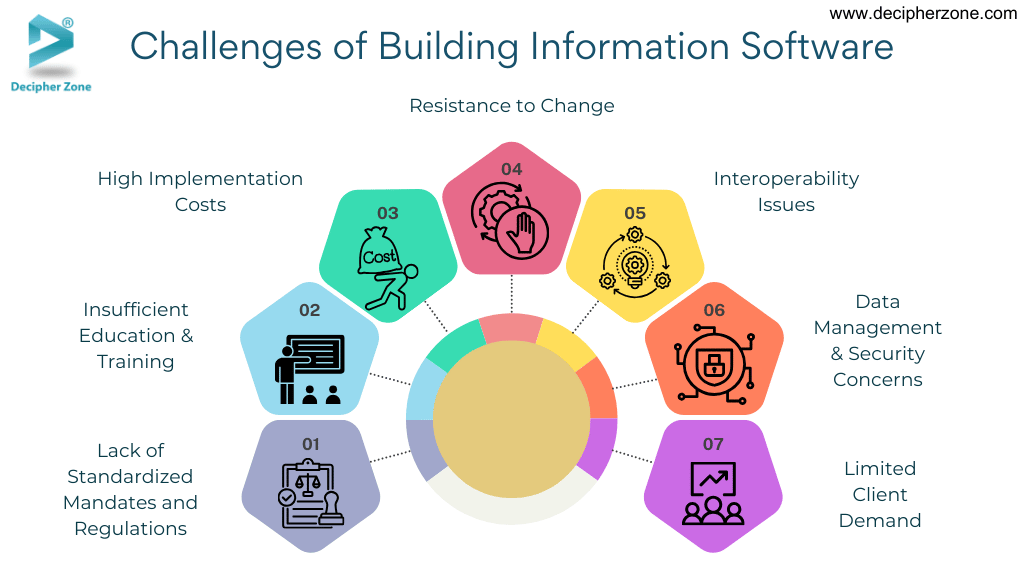
Challenges of Implementing BIM Software
Here are the challenges businesses face:
-
Lack of Standardized Mandates and Regulations
-
Insufficient Education & Training
-
High Implementation Costs
-
Resistance to Change
-
Interoperability Issues
-
Data Management & Security Concerns
-
Limited Client Demand
Building Information Modeling (BIM) implementation is not without challenges. Understanding these hurdles is crucial for stakeholders aiming to utilize BIM’s full potential.
1. Lack of Standardized Mandates and Regulations
While some nations have implemented BIM requirements for public projects, many others lack clear guidelines that cause confusion and impede widespread implementation. The absence of universal BIM standards and mandates across different countries and regions leads to inconsistent adoption.
Experience the future of construction and design. Get started with our next-generation BIM software today
2. Insufficient Education & Training
The workforce can lack the necessary skills as many architecture and engineering curricula do not comprehensively cover BIM. This educational gap makes it challenging for firms to find qualified professionals which slows down BIM adoption.
3. High Implementation Costs
BIM software requires initial investment, hardware upgrades and training which can be substantial. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often find these costs prohibitive and can delay or prevent BIM integration into their workflows.
4. Resistance to Change
Transitioning to BIM requires a shift in traditional workflows and mindsets. Some professionals are resistant to adopting new technologies, preferring established methods which can impede the integration of BIM into organizational processes.
5. Interoperability Issues
Different BIM software platforms may not allow to seamlessly communicate with each other which leads to data exchange problems. This lack of interoperability can cause information loss, errors and inefficiencies during project collaboration.
6. Data Management & Security Concerns
BIM models pose challenges in storage, organization and security as they manage the vast amount of data generated. Ensuring data integrity and protecting sensitive information are critical concerns that need to be addressed.
7. Limited Client Demand
The lack of motivation can discourage firms from investing in BIM software as clients are not fully aware of the benefits of BIM and do not demand its use.
Industry stakeholders, educational institutions and policymakers require concerted efforts to address these challenges. By developing standardized regulations, enhancing education and training programs and promoting the tangible benefits of BIM, the AEC industry can overcome these obstacles and fully realize the advantages of BIM technology.
Read: Improve Your Software Development Team’s Productivity
How Can We at Decipher Zone Assist You in BIM Software Development?
Whether you are an AEC firm looking to digitize your workflows, a construction company or a business seeking to invest in software that streamlines operations, we offer the technical expertise and industry insights essential to turn your vision into reality and enhance project coordination.
At Decipher Zone, we specialize in developing robust, scalable and intelligent software solutions tailored to support Building Information Modeling (BIM) across various industries with a primary focus on architecture, engineering and construction. Here’s how we help you explore the full potential of BIM:
Custom BIM Software Development:
We build fully customized BIM tools that align with your project requirements from 3D modeling and data integration to collaboration and simulation features.
Seamless System Integration:
Our software solutions ensure smooth interoperability with existing platforms like CAD, ERP and project management tools, eliminating data silos and inefficiencies.
AI-Powered Analytics & Automation:
We embed intelligent features such as AI-based clash detection, predictive analytics and real-time resource tracking to enhance accuracy and productivity.
Cloud-Based Collaboration Platforms:
Provides real-time communication and data sharing between architects, engineers, contractors and stakeholders across locations.
Sustainable and Scalable Solutions:
We help you meet sustainability goals while building future-ready applications from energy performance simulations to lifecycle asset management.
End-to-End Support:
Our team stays with you every step of the way from ideation and development to deployment and post-deployment, ensuring the solutions evolve as your needs grow.

Decipher Zone is here to help you lead the BIM revolution. If you’re ready to modernize your construction workflows, enhance decision-making and deliver projects faster and smarter. You are at the right place.
FAQs
-
What is Building Information Modeling (BIM) Software?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) Software is a tool that allows AEC industry teams to design, manage and execute projects by developing, analyzing and managing digital representations of physical and functional buildings of places. BIM brings together multiple disciplines architecture, engineering, construction and facility management onto a shared, intelligent 3D model.
-
What are the core services available in the Building Information Modeling (BIM) software market?
The key use cases of Building Information Modeling (BIM) are 3D visualization & design simulation, clash detection and coordination, cost estimation and budget management, construction sequencing & scheduling, facility management & operations, streamlined fabrication & prefabrication processes, regulatory compliance & code reviews and disaster planning and emergency management.
-
What are the challenges in implementing BIM software?
There are various challenges in implementing BIM software including a lack of standardized mandates and regulations, insufficient education & training, high implementation costs, resistance to change, interoperability issues, data management & security concerns, limited client demand, etc.

